这篇文章是我做毕设的时候发现的,也是我最初学到的医学领域上的一些指标,遂记录下来以防忘记,如不慎侵权请联系我。
This page was found by me during my senior year, in case I forget, I reproduce this article now. If there is an infringement, please contact with me (903394428@qq.com)
original website from:https://step1.medbullets.com/stats/101006/2x2-tables-sn-sp-ppv-npv-or-rr
First of all ,we can know TP,FP,FN,TN vias a picture below.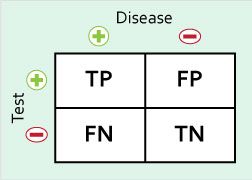
Index
Sensitivity, Specificity, PPV, NPV
These 4 measures describe how well diagnostic tests capture the true presence or absence of disease.
- Sensitivity (SN)
- % with disease who test positive
- = a/(a+c) = TP/(TP+FN)
- Specificity (SP)
- % without disease who test negative
- = d/(b+d) = TN/(FP+TN)
- Positive predictive value (PPV)
- % positive test results that are true positives
- = a/(a+b) = TP/(TP+FP)
- Negative predictive value (NPV)
- % negative test results that are true negatives
- = d/(c+d) = TN/(FN+TN)
Cut-off point may be adjusted to optimize sensitivity and specificity, which are inversely related (cut-off point with decreased sensitivity is associated with increased specificity and vice-versa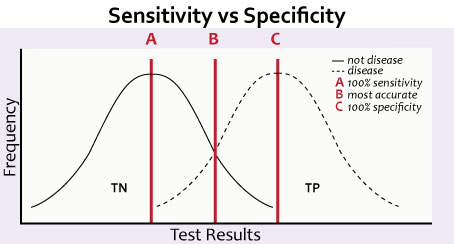
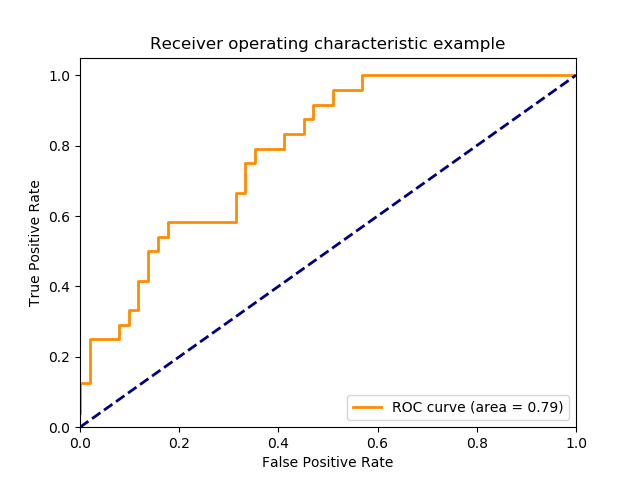
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC)
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves are a graphical depiction of a test’s performance
- Y axis: sensitivity
- X axis: 1-specificity ( which is the same with FP / ( FP + TN) )
- The higher the curve, the better the test
- This is quantified by the AUC (area under the curve); an AUC of 0.5 states that the test performs no better than chance (bad test!), whereas an AUC of 0.9 suggests a better-performing test
- The curve passes through ( 0, 0 ) point by default
free receiver operating characteristic (FROC)
free receiver operating characteristic (FROC) curves are a graphical depiction of a test’s performance , compared with the ROC curves, it is more suitable for the condition where the number of positive and negative samples is uneven extremely
- Y axis: sensitivity
- X axis: FPs (the number of FP samples)
- More the area under the curve, better the test
- This is quantified by the AUC (area under the curve), same with the FROC
- The curve passes through ( 0, 0 ) point by default
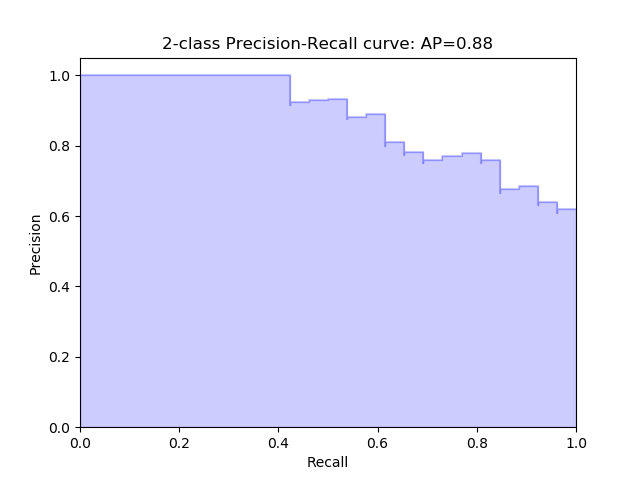
precision recall curve (PRC)
Curve based on precision-recall pairs for different probability thresholds,compared with the ROC curves, it is more suitable for the condition where the number of positive and negative samples is uneven extremely
- Y axis: precision (TP / (TP + FP))
- X axis: recall (same with the Sensitivity)
- More the area under the curve, better the test
- The curve passes through ( 0, 1 ) point by default
f1-score
F1 score (F1 Score) is an index used to measure the effect of the two classification models in statistics. It also takes into account the precision and recall of classification models. The F1 score can be regarded as a weighted average of the accuracy and recall of the model. Its maximum value is 1 and the minimum value is 0.
Odds Ratio, Relative Risk, Attributable Risk
These measures describe the relationship between a risk factor and a disease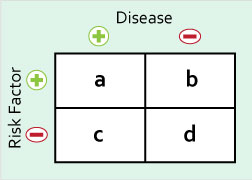
Odds Ratio (OR)
- odds of having disease in expose group / odds of having disease in unexposed group
- = ad/bc
- odds of having disease in expose group / odds of having disease in unexposed group
Relative Risk (RR)
- probablity of getting disease in exposed group / probability of getting disease in unexposed group
- = [a/(a+b)] / [c/(c+d)]
- probablity of getting disease in exposed group / probability of getting disease in unexposed group
Attributable Risk (AR)
- risk in exposed group - risk in unexposed group
- = a/(a+b) - c/(c+d)
- risk in exposed group - risk in unexposed group